Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is to a delayed radiation injury characterised by bone necrosis and failure of wound healing for at least 3-6 months, may result from radiotherapy alone or in combination with a mechanical insult.
The condition most often occurs after radiotherapy (iatrogenic) and might be referred to as post-radiotherapy osteonecrosis, ocurring on average 2-4 years after completing the therapy with an incidence of 3%.
Two complementary theories exist to describe the pathogenesis:
Marx’s theory describes a process of radiation-induced hypovascularity, hypoxia, and hypocellularity.
The fibroatrophic theory says that radiation damage induces fibroblast dysregulation leading to inability to repair tissue damage.
Usually, large radiation doses are required for it to occur (30-60 Gy), the higher the dose, the more likely that ORN will occur.
Specific sites in which osteoradionecrosis is more commonly seen:
- Mandible.
- Chest wall - shoulder - humerus - scapula.
- Spine.
- Pelvis.
Why bone specifically? As there is a more robust and redundant blood supply to mucocutaneous membranes than to bone and cartilage, the former tends to heal with time, while the latter may have a protracted or arrested healing course. Radiotherapy can additionally cause progressive obliterative endarteritis, as well as hindering the capillary regrowth of normal healing.
- Mandibular ORN; Symptoms: persistent painful oral ulcer, odynophagia, pain-related trismus, occlusal changes (how the upper and lower sets of teeth fit when the mouth is closed), a foreign body sensation in the mouth, expectoration of bone chips, halitosis.
Tooth extraction should occur at least two weeks before radiotherapy. Optimal dental health is necessary to lower the risk.
Treating diagnosed ORN requires surgical intervention, the bone must be debrided down to healthy, bleeding bone. Local flaps, regional or free flaps, and segmental mandibulectomy with vascularised bone flap reconstruction are some of the possible routes of management, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is also used to promote angiogenesis in hypoxic tissues, thus promoting optimal reparative conditions.
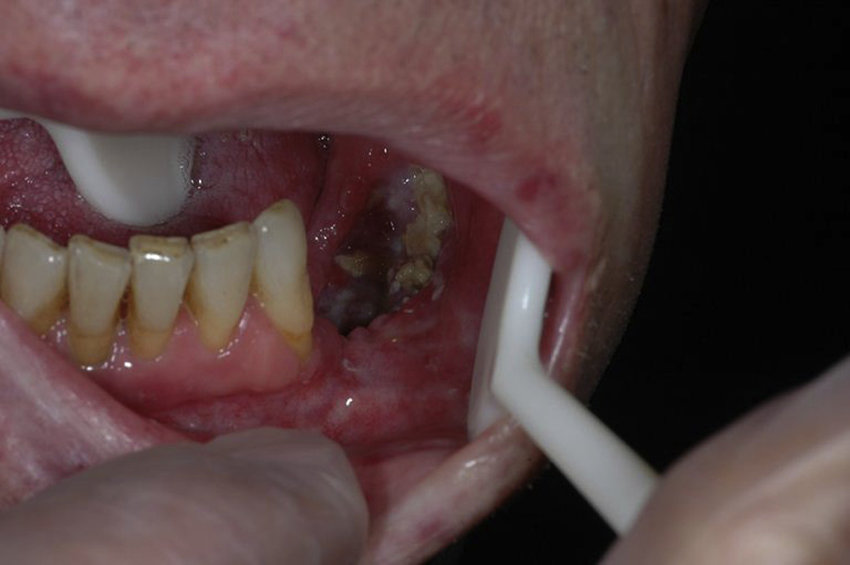 Exposed mandibular bone 12 months after molar extraction
Exposed mandibular bone 12 months after molar extraction